Opinion
Lagos-Calabar Highway Must Wait
Had the Presidency not responded to the allegations of the former Vice President, Atiku Abukakar, concerning the process of awarding of the contract for the Lagos-Calabar Coastal Highway, it would have been most surprising. People must do the job for which they were employed and that includes ensuring at all costs that their principals and their families are constantly blameless and spotless.
Atiku, through his Media Adviser, Paul Ibe, had alleged that President Bola Tinubu’s son, Seyi Tinubu, being a board member of one of the firms owned by Gilbert Chagoury, the owner of Hitech, the contractor that was awarded the contract constitutes a conflict of interest; that the contract was awarded in contravention of the procurement laws, that it is being done in a hurry purely because of the business relationship between President Tinubu and Gilbert Chagoury, that the project is expensive, ill timed among others.
But in a swift response the presidency through a statement by the Special Adviser to the President on Information and Strategy, Bayo Onanuga, countered Atiku’s claim, saying that as an adult Nigerian, Seyi has the right to do business in the country and that his membership of the board of CDK in no way constitutes a conflict of interest.
Onanuga went down the memory lane, recounting how the former Vice President had revealed that he formed Intels Nigeria with an Italian businessman when he was serving in the Nigeria Customs Service, which in his view is a clear breach of extant public service regulations; how, as Chairman of the National Council on Privatisation, Atiku approved sales of over 145 State-owned enterprises to his known friends and associates and openly said during his failed campaign for the presidency last year that he would do the same, if elected.
The Special Adviser dwelt so much on Atiku’s past that he probably forgot to address some other key issues raised by the former VP about the Lagos-Calabar Coastal Highway project which had also been harped on by several other Nigerians. First is the issue of the contract’s awarding process and priority. Nigerians needed to hear directly from the presidency whether this huge project went through a competitive bidding process as required by law or not. Section 16 (1) (c) of the Public Procurement Act 2007 provides that “All public procurement shall be conducted by open competitive bidding.” Section 16 (1) (d) stipulates that all public procurement shall be done in a transparent, equitable manner to ensure accountability. Was the contract awarded in compliance with this and other relevant laws?
There is also the issue of the highway project not complying with the Environmental Impact Assessment Act. The Pan-Yoruba Socio-Political Organisation, Afenifere, had through Prince Jide Faloye of its Publicity Department joined some other groups and individuals to raise concern about the serious issue. The organisation said, “The Lagos-Calabar Coastal Highway project must be re-examined, for not only breaching competitive tendering stipulations but for also contravening the Environmental Impact Assessment Act, as stipulated in EIA Decree No. 86 of 1992, which places the project type in Category 1 and affecting the natural environment, making an ESIA report mandatory before commencement.”
Afenifere also noted that, “the $13 billion Lagos-Calabar project is not only environmentally and economically destructive, but also irrationally replaces the 1,400km $12 billion Lagos-Calabar railway project along East-West Road, adjudged to be the single most important economically empowering infrastructural development project in Southern Nigeria in over 100 years, commissioned by both the Jonathan (2014) and Buhari (2021) governments.”
Convincing explanations to their salient concerns are what Nigerians want from the presidency, the Minister of Works, Dave Umahi and other relevant authorities instead of them resorting to name calling and describing the views as “ intrinsically superficial, baseless, self-serving and politically motivated to imprint malice in the minds of unsuspecting members of the public, especially the gullible”, as the Special Adviser (Media) to the Minister of Works, Orji Uchenna Orji did in a statement a few days back.
Government is all about the people. Fortunately, Nigeria is operating a democratic system of government widely known to be the government of the people, by the people and for the people. Therefore, the leaders put in power by the people should listen to the people and should always prioritise the interest of the people.
And talking about priority which was among the issues raised by Atiku, is the Lagos-Calabar highway the most critical need of the country right now? Yes, the road when completed will be of immense benefit to the coastal states and the country in general. Economic growth, easy transportation, improved quality of life will be assured, but is that what we need now in Nigeria? Two weeks ago, Rivers State and the entire nation were thrown into mourning as a result of the vehicular accident that happened in the Eleme axis of the East-West which claimed several lives and damaged property. The lamentation of many people, including the State Governor, Siminalayi Fubara, was that the accident and the great losses could have been avoided had the road been fixed.
The about 328-kilometer road which was awarded in 2006 by the then President, Olusegun Obasanjo, and meant to be completed in 2010 is yet to be completed despite the billions of Naira that has gone into it. The Enugu-Onitsha road, Makurdi-Enugu road, Port Harcourt-Enugu express road and many other federal roads across the country have long become death traps. People have protested, demonstrated, appealed to the authorities to have them fixed, yet little or nothing has been done on most of them.
Could it not have been better to fix these roads before embarking on a new road that will cost nothing less than N2.8 trillion? A ready answer by the works minister and other government functionaries might be that N300 billion was provided in the 2023 supplementary budget to address the poor federal roads but how far can that go?
There is undoubtedly nobody in Nigeria that is not feeling the pinch of the current harsh economic realities in the country. Prices of food and other items in the market keep skyrocketing every day. The cost of transportation has quadrupled since May 29 when the announcement that “subsidy is gone” was made. For some weeks, there has been fuel scarcity in Abuja and other parts of the country which the Nigerian National Petroleum Corporation Limited (NNPCL) blamed on “logistic issues”.
The NNPCL keeps shifting the goal post on when Port Harcourt, Warri and Kaduna refineries will become operational. The latest being that the Port Harcourt Refinery will start functioning by the end of March. In the second week of March, the Group Chief Executive Officer (GCEO) of the (NNPC) Mele Kyari, reportedly told the senate ad hoc committee investigating the various turnaround maintenance (TAM) projects of Nigerian refineries that, “In the next two weeks, production will start. We did mechanical completion of Port Harcourt Refinery, that was what we said in December 2023,”
“That means we are done with our rehabilitation work, now you are to test if this completion is okay.” Has this happened?
The point is that the federal government should suspend the massive, flamboyant Lagos-Calabar coastal highway project pending when the economy is up and running and some critical infrastructure in the country are adequately attended to. If part of this huge sum could be used to build new refineries and make the old ones bounce back to life, Nigeria will be on the way to achieving energy security which will impact positively on every sector of the economy and the lives of the citizens. Efficient and transparent use of the nation’s scarce resources is an important quality that our leaders must imbibe.
Calista Ezeaku
Opinion
Nigeria’s Electricity Sector: Need For Restructuring
In mid October, 2024, our national electricity grid suffered three collapses just within a week, throwing many states of Nigeria in total blackouts. Right from independence, Nigeria has always set agendas for attaining steady electricity, but ends up failing to achieve that noble objective. The perennial challenge of providing reliable electricity across Nigeria is however no puzzle beyond humans, yet the sector remains backward, notwithstanding series of reforms and public expenditures. But at the centre of the failures from all past reforms, is a common factor – the reluctance by government, whether deliberate or inadvertent, to extricate itself from the operational lines of the business. The presence of Nigerian government in any business process, especially where it monopolistically occupies vital operational linkage, has proven to create bottlenecks that stifle efficiencies, and defeat the overall objectives.
This was evident in the telecommunications sector, as it is in the petroleum and power sectors. Take for instance, the current policy framework that overshadowes electricity business across Nigeria, where in the name of privatisation, government deliberately butchered off, and separately sold vital organs of the national electricity industry, in an arrangement where the generating companies (GenCos) do not have licences to transmit and distribute generated power, and distribution companies (DisCos) have no licences to produce the sole commodity they sell, while the federal government through the Transmission Company of Nigeria (TCN), monopolistically retains transmission trades between GenCos and DisCos.The insertion of TCN between the private businesses of power generation and distribution, destroys benefits derivable from privatising electricity productions in Nigeria.
With the GenCos and DisCos answerable to the separate managements while the TCN reports to the Federal Ministry of Power, Works and Housing, it is obvious that the unbreakable chain of commands needed for seamless business operations was designed for disarray. Besides, government also solely holds the stakes in gas supplies needed for much of Nigeria’s 16,384 MegaWatts installed capacity. Due to inadequacy of gas supplies, the GenCos produce about 8,415MW, out of which, due to TCN’s inefficiency, only about 4,000MW get to DisCos. However, among the three loosely bound entities in Nigeria’s unholy marriage of electricity production, the GenCos appear more upbeat at investing for increased capacity but are dragged by delivery challenges from the TCN on the one hand, and poor revenue returns from the DisCos, on the other.
The failure of TCN to deploy modern surveillance and field data acquisition technologies to maintain network reliability, has left its facilities prone to vandalism. It does not encourage GenCos who take the major production risks that they can not deal directly with consumers. In the prevailing situation in which DisCos, being closest to power consumers harvest the collective revenue, the opaque nature of that crucial assignment as currently being conducted, gives room for under-reporting.The electricity business like any other, should project transparent prospects of profits to inspire undertakings in investment risks, and it is only operational frameworks that assure investors of end-to-end process integrity that can encourage the deployment of total commitments. Discos’ obvious reluctance at metering, nor upgrading distribution facilities for efficiency, gives no incentives to GenCos to increase investments in power generation.
It does not also help that TCN’s Market Operations (MO) department passes revenue trickles from DisCos, unto GenCos without enforcing collection transparency on the former. Most of Nigeria’s electricity transmission network infrastructure were installed more than 50 years ago. Since inheriting the transmission assets in the 2005 privatisation, and further restructuring in 2013, TCN’s Transmission Service Provider (TSP) department which is responsible for grid construction and maintenance has not done much to expand network capacity in readiness for increased generation. Neither has its System Operations (SO) department, responsible for stabilising operations, upgraded its frequency management and switching capabilities, but still relies on manual switching instead of investing in Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems that respond swiftly to changing grid frequencies.
It was not surprising therefore that a usual process fluctuation that came from uploading increased power generation into the national grid had overwhelmed SO’s manual switching capability, leading to the grid collapse of October, although Minster of Power alluded to the fact that the inability of TCN’s aged infrastructure to absorb extra power caused explosions at Jebba sub-station, leading to instabilities that collapsed the grid. Which ever be the case, the buck stops at the TCN, and by extension at government. One may then question the benefits derivable from contracts signed by the Buhari administration with Siemens of Germany in 2019. System automation is undeniably the core expertise of Siemens, and the deployment of the company’s switches would have handled grid fluctuations to prevent any collapse. Despite the huge budget allocations that go into the ministry of power, it is obvious that government processes – encumbered by bureaucracy, politics, paucity of funds and lack of business savvy – is entangling TCN’s abilities at keeping pace with its private partners.
So why should government create such a clog in the wheels of progress? Moreso, it has never been known that government declared financial profits from its years of investments in the power sector, nor are the social benefits apparent. Rather than hold unto an asset that continuously drains scarce finances at no benefits, while creating bottlenecks to processes, government should completely hands-off the industry, focus on its regulatory roles, and draw tax accruals. According to estimates by the World Bank, the failure of reliable power supplies in Nigeria costs yearly losses of $29 billion to companies who had to produce their own power, and is a major reason most companies close down in the country, or have migrated elsewhere, despite our human resource potentials and Nigeria being a huge market. The current Nigeria Electricity Supply Industry (NESI) structure, in which government-owned TCN is sandwiched between disunited GenCos and DisCos, is causing conflict of interests, unsustainable and ensures a tie of stagnation.
The electricity production framework should be restructured, even if it means partitioning the national grid, into a form that gives power companies combined and seamless abilities to generate, transmit and distribute power directly to their consumers, as being experimented by the Geometric Group in Aba.
Joseph Nwankwor
Opinion
“Ye Are Gods”: A Contemporary Review
The phrase “Ye are gods”,as contained in Psalm (82:6) and reiterated by Jesus in John (10:34), has been a major source of controversy in humanity. Taken alongside the biblical assertion “God created man in his own image and likeness” (Genesis 1:26) it sums up to Rev STK Appah’s posit that “what is in the original is in the creation”. Over the years, divergent views have been adduced on this contentious issue, which violently tugs at the roots of our belief system. Come, share my thoughts. In a one-man live-in protest over a discriminatory housing policy at Murray State University, Murray, Kentucky, USA, I occupied the six-floor Hart Hall (men’s hostel) during Thanksgiving Holiday of 1974. At the end of that effort, I wrote a poem titled “Why can’t we live together” and an article and submitted both to Murray State News, the university newspaper. The article, which vociferously decried the policy, was published with the title “Student Speaks Out” on December 6, 1974, but the poem was not. The essence of the poem said: “Some Beings are watching us to see how we get on/Let’s pull forces together and live in oneness”.
My take on the rejection of the poem was the fact that, irrespective of President Eisenhower’s triple liaison with aliens in New Mexico in 1954 and the strange crash on July 7, 1947 at Roswell, New Mexico, Americans were living in denial of an advanced civilization in the cosmos. Sadly, humanity still lives in that denial. In 2006, I wrote “In His Image and Likeness: Pondering Over Creation and the Divine Essence”. Drawing from the scriptures, I contended that “man is of equi-potentiality with his Creator who is not the multi-Omni Spirit Being…[and that] in the endlessness of eternity, man will also create in his image and likeness”. At the heels of the article, which was published by MELINTAS—Journal of Philosophy and Religion at Parahyangan Catholic University of Indonesia, I received fifty-eight hate mails and twenty-nine support mails. The hate mails pronounced the equivalent of fatwa on me; one of the support mails commended my “liberated mind”.
Today, Geoffrey Hinton, the acclaimed Godfather of artificial intelligence (AI), has quit his job at Google and has warned humanity of the dangers of AI. Asked if humanity knows what it is doing with AI, Hinton offered a definitive “No” and added that “We may have created something more intelligent than us”. Hinton furthers that AI can understand, has intelligence and experience and can make decisions on its own based on those experiences “in the same sense as humans do.”. The scary part is that Hinton thinks that, in time, AI will become conscious of its existence, rewire its circuits and become more intelligent than man; then, humans will become the second most intelligent beings on earth. Meanwhile, Elon Musk says that his “Citigirl”, an AI with the capacity of incubating and delivering a baby, will hit the marketplace in 2026. These are godly feats.
The above is reminiscent of the allegory of Tower of Babel. The Creator in the Babelian episode was surprised and sufficiently threatened by man’s exploits hence the infliction of the scourge of linguistic plurality on the human brain. Notedly, this fear-induced act of self preservation by the Creator, introduced conflict amongst the hitherto monolingual Babelian workforce that worked harmoniously towards building “a city, with a tower that reaches to the heavens” (Gen 11:4). The truth remains that, in the universal context, we are dealing with a hierarchy of Gods and there are millions of inhabited planets in the Cosmos; Jesus alluded to this thus: “In my father’s house there are many mansions” (John 14:2). Planet earth is just a tiny little speck of sand on the sprawling beach of creation. The fear of the capacity of AI and the regret expressed by Geoffrey Hinton are reminiscent of the Creator’s expressed regrets for creating man (Genesis 6:6) and palpable fears at Babel (Genesis 11:1-9).
It is also a reminder of Dr. Frankenstein’s experience with the monster he created. So, it is asked: Is humanity at the verge of an encore of the Babelian exploit? If so, is the Creator likely to intervene? AGAIN?! Man is certainly at the threshold of a profound experience. All said, man has reached a major milestone in his quest to “dominate his environment”. However, he has toed the path of perdition. Here, Thomas Paine’s philosophy of “doing good” as a religion and “the world” as his country is the required mindset for humanity. Taken alongside the Humanist school of thought and the objectives of Universal State of Earth (USE), perhaps man will find global harmony and depart from his self-destruct trajectory. The Creator of man is not the multi-Omni Being . Man’s Creator is the plurality that created in their image and likeness at Eden; they may be the same ones that were surprised and scared at Babel and the Lords of Ezekiel’s encounters.
The larger picture is that we are gods and can also create in our image and likeness. Man is much more than he realises. Given the elasticity and rewireability of the brain, man is yet to achieve the godly potential of his God-given brain. So, “Let’s get forces together and live in oneness” by putting our lights on and training our children to leave their lights on. That way, we would transcend matter, heal the world and take our proper place in the universal hierarchy of gods.
Jason Osai
Osai wrote in from Port Harcourt.
Opinion
Child Rape: A Global Menace
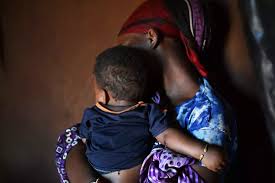
Child rape is a profound human right violation that inflicts lasting physical, emotional, and psychological scars on its victims. Among the most vulnerable groups, the girl-child faces a disproportionate amount of sexual abuse globally, reflecting deep-rooted societal, cultural, and systemic failures. Despite international laws and local measures aimed at protecting children, rape and sexual violence against girl-child remain a pervasive problem in many parts of the world, as it is alarmingly prevalent worldwide. According to data from the World Health Organisation (WHO), one in four girls experiences some form of sexual abuse before the age of 18. This abuse occurs across all socio-economic, cultural, and geographical divides. The underreporting of sexual violence against children, fueled by fear, stigma, and victim-blaming, makes it difficult to grasp the true scale of the problem.
Reports from organisations like UNICEF and Human Rights Watch highlight that in some regions, girl-children are specifically targeted due to the belief that they are “pure” or “virgin,” making them more vulnerable to cultural myths that suggest intercourse with a virgin can cure diseases like HIV/AIDS. These deeply harmful beliefs exacerbate the risk for young girls, particularly in countries where educational and legal protections are weak.A range of factors contributes to the high incidence of rape against girl-children, many of which are embedded in patriarchal and misogynistic beliefs. In some cultures, girls are viewed as inferior or subservient to males, making them easy targets for exploitation. The normalisation of gender-based violence in some communities means that abuse often goes unnoticed, unreported, or unpunished. Child marriage, which remains prevalent in some parts of Africa, Asia, and the Middle East, is another contributing factor.
When girls are married off as children, they are often exposed to sexual violence under the guise of marital relations. These young brides, who are typically powerless in these situations, often endure repeated sexual abuse from their significantly older husbands.Additionally, in conflict zones, girl-children are disproportionately affected by sexual violence, used as tools of war by armed groups to terrorise communities. Such exploitation results in severe trauma and long-lasting consequences for victims. Rape and sexual abuse leave devastating effects on a girl-child, both physically and mentally. Physically, young girls are not developed enough to handle sexual intercourse, leading to severe injuries, infections, and even death in extreme cases. Many victims also face long-term reproductive health issues, including infertility, sexually transmitted infections (STIs), and complications in future pregnancies.
The psychological toll is equally profound. Victims often suffer from depression, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and other mental health conditions. The stigma associated with sexual violence further isolates them from their families and communities, leaving them vulnerable to further exploitation or abuse. The educational consequences are also significant. Many victims drop out of school due to the trauma, fear of facing their abusers, or the stigma attached to rape. This creates a cycle of poverty and dependence, further reducing their life chances. Access to justice for child rape victims is often fraught with challenges. In many countries, laws around sexual violence are outdated, under-enforced, or not well understood. Law enforcement agencies frequently lack the training or resources to handle cases of child sexual abuse appropriately, leading to further victimisation during investigations.
In some cases, cultural practices such as “settling” rape cases between families, or forcing victims to marry their rapists, prevent victims from receiving the justice they deserve. This, not only robs the victim of justice but perpetuates a culture of impunity where perpetrators feel empowered to commit further acts of violence. Additionally, the social stigma surrounding rape prevents many girl-children from coming forward. Fear of blame, retaliation, or being ostracised by their communities often keeps victims silent, allowing abusers to continue their crimes unchecked. Internationally, the United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child (UNCRC) and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) both call for an end to all forms of violence against children, including sexual abuse. Organisations such as UNICEF, Plan International, and Save the Children, have been instrumental in raising awareness, supporting survivors, and lobbying for stronger laws and protections.
On a national level, many countries have taken steps to strengthen legal frameworks to protect children from sexual violence. Child protection laws, survivor-centred legal reforms, and harsher penalties for offenders have been introduced in several countries. However, effective implementation remains a challenge in many places due to corruption, weak legal systems, and deep-seated cultural barriers. To truly address the epidemic of child rape, a multi-faceted approach is needed that tackles the root causes of the problem. Education and Empowerment of girl-children can go a long way in preventing rape cases in the society. Educating girls about their rights, providing them with life skills, and empowering them to speak out against violence are crucial steps in preventing abuse. Equally important is educating boys and men about consent, respect, and gender equality to shift harmful patriarchal norms.
Girls and women need stronger legal protection to escape some of the rape cases that occur regularly. Governments must prioritise the implementation of robust child protection laws, ensuring that law enforcement agents are well-trained and sensitised to handle cases of child rape. Special courts for handling cases involving children, victim support services, and protective measures should be readily available to survivors. If we have to curb child rape menace, community engagement must be included in the process. Engaging communities to change attitudes toward girl-children and dismantling harmful gender norms is essential. Community leaders, religious figures, and educators can play a pivotal role in shifting mindsets and promoting zero tolerance for violence against children.
Furthermore, there is the need for support for survivours of rape. Comprehensive support systems for survivors are critical for the rest of their lives. These include access to psychological counselling, medical care, legal aid, and safe spaces where victims can heal and rebuild their lives. Schools should also provide supportive environments to help victims continue their education without fear of stigma or discrimination. Global Advocacy and Accountability from World Health Organisation (WHO), UNICEF, and other relevant agencies should as a matter of fact continue to create more awareness and sensitisation on the need to save the girl-child. International organisations and governments must continue to advocate for the protection of children’s rights, ensuring that perpetrators are held accountable. Monitoring mechanisms, transparency in legal proceedings, and collaboration between countries are key to fighting transnational issues like child trafficking for sexual exploitation.
It is worrisome to note in the 21st century, as the world is a global village, fully digitalised, when the girl-children should be allowed to showcase their potentials, instead they are trafficked to do jobs that will harm their lives. Parents particularly, should have the number of children they can cater for. They should also pay attention to the ones they have. Moreso, the boy-children and the men should be sensitised on the need to stop the menace. Rape and sexual violence against girl-children are some of the gravest injustices of our time, robbing millions of their childhoods and futures. While progress has been made, there is still much work to be done to protect the most vulnerable among us. It is only through collective action, from governments, communities, families, and international organisations, that we can create a world where girl- children are safe, empowered, and free from violence.
By: Perpetual Izuegbunam
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoForge Unity For Progress, Fubara Urges Nigerian Youths …Accepts Beacon Of Hope Award
-
Politics3 days ago
Inclusivity: Chief Whip Makes Case For Women
-
Sports3 days ago
Subsea Cycling Club Chairman Solicits For Support
-
Nation3 days ago
Director Tasks ICAD Members On Professionalism
-
Rivers3 days ago
Ministry Debunks Akpana’s Leadership Of JONAPWD … Sets Stage for Peaceful Election
-

 Editorial3 days ago
Editorial3 days agoA New Dawn For Rivers’ Workers
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoNADF, NASC Partner To Boost Food Security
-

 Politics3 days ago
Politics3 days agoGanduje Gets February 13 Date For Hearing In Alleged Bribery Trial

